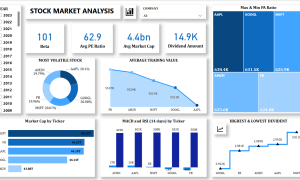
Power BI for data modeling
Data modeling is the backbone of any successful Power BI project, allowing you to transform raw data into meaningful insights. Power BI’s robust features, including the “Relationships” view and support for DAX (Data Analysis Expressions), make it a leading choice for data analytics professionals. In this blog, we’ll explore the critical aspects of data modeling in Power BI and share actionable tips to enhance your analytical solutions.
1. Relationships Management
Power BI simplifies the process of defining relationships between tables using an intuitive visual interface. This enables seamless querying and calculations across related tables.
Key Aspects
- Star Schema Design: Organize your data into fact and dimension tables for better performance.
- Relationship Types: Accurately define one-to-many and many-to-one relationships.
- Cardinality Settings: Choose single or bidirectional cross-filtering based on your analytical needs.
Solutions
- Clean Your Data: Before importing, ensure data consistency and relational integrity.
- Manage Relationships: Use Power BI’s “Manage Relationships” feature to define and adjust relationships.
- Validate with Visualizations: Use simple visuals like tables or matrices to verify relationship accuracy.
2. Mastering DAX (Data Analysis Expressions)
DAX is the language that powers Power BI’s calculated columns, measures, and tables, enabling dynamic data manipulation.
Key Aspects
- Measures: Use aggregation functions like
SUM,AVERAGE, andCALCULATEfor efficient calculations. - Time Intelligence: Apply functions like
DATEADDandTOTALYTDfor advanced date-related analytics. - Logical Functions: Create custom conditions using functions like
IFandSWITCH.
Solutions
- Learn Common Patterns: Understand filtering, context transition, and row context.
- Keep It Simple: Name your measures clearly and avoid overly complex formulas.
- Test Iteratively: Break down formulas into smaller parts to ensure correctness.
3. Data Transformations with Power Query
Power BI’s Power Query Editor offers powerful tools for shaping your data before modeling.
Key Aspects
- Data Cleaning: Remove unnecessary columns and clean datasets for efficiency.
- Normalization: Simplify relationships and reduce redundancy.
Solutions
- Preprocessing in Power Query: Merge, split, and aggregate tables as needed.
- Optimize Data Loads: Perform transformations to minimize load times and improve performance.
4. Performance Optimization
Large datasets and complex relationships can hinder performance. Power BI provides tools and strategies to tackle these challenges.
Key Aspects
- Large Datasets: Excessive data volume can slow down reports.
- Inefficient DAX Queries: Poorly written DAX can consume excessive resources.
Solutions
- Use Aggregated Tables: Pre-calculate data to simplify queries.
- Reduce Cardinality: Group data where possible to improve efficiency.
- Monitor Performance: Leverage the Performance Analyzer to identify bottlenecks.
5. Ensuring Data Security
Data security is a top priority, especially when handling sensitive information.
Key Aspects
- Row-Level Security (RLS): Restrict data access based on user roles.
Solutions
- Define RLS Roles: Use Power BI Desktop to configure roles.
- Test Thoroughly: Verify security settings before publishing to the Power BI Service.
Conclusion
By focusing on relationships management, mastering DAX, leveraging Power Query, optimizing performance, and securing your data, you can unlock the full potential of Power BI for data modeling. These practices not only enhance efficiency but also ensure accurate, scalable, and secure analytical solutions. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, these techniques will empower you to make the most of Power BI’s capabilities.